2017-01-05
章轲 京环之声
Some people say that gasoline car emissions can purify the air and have little impact on the formation of haze. Some even believe that car exhaust is cleaner than hazy air. These statements are incorrect and misleading, "Ge Yunshan, director of the National Professional Laboratory for Automotive Power and Emission Testing at Beijing Institute of Technology, told First Financial reporters on the morning of the 5th.
Recently, a video circulating online showed that a portable instrument was used to measure the emissions of gasoline vehicles in smog. The results showed that the concentration of PM2.5 in gasoline vehicle exhaust was lower than that in the air, leading to the conclusion that gasoline vehicle emissions can purify the air and have little impact on the formation of smog.
Ge Yunshan told First Financial reporters that the test results in the video have some reasonable elements, but the testing process and result analysis are not yet fully scientific, and a comprehensive, scientific, and objective view of gasoline vehicle pollution is needed.
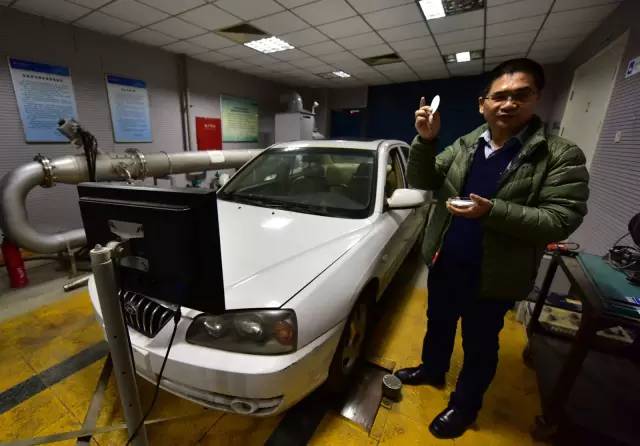
On the morning of the 5th, the First Financial Journalist rushed to the National Professional Laboratory for Automotive Power Performance and Emission Testing on the campus of Beijing Institute of Technology. The laboratory is mainly engaged in teaching and research on emission control of internal combustion engines and mobile pollution sources.
Entering the laboratory gate, the reporter saw a white Beijing Hyundai 1.8-liter sedan parked on the testing line, and the technicians were also ready for testing.
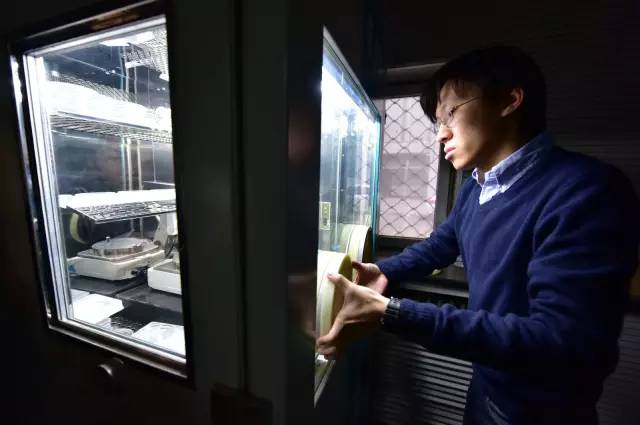

Technicians weigh filter paper using a constant temperature and humidity weighing box. Photography/Zhang Ke
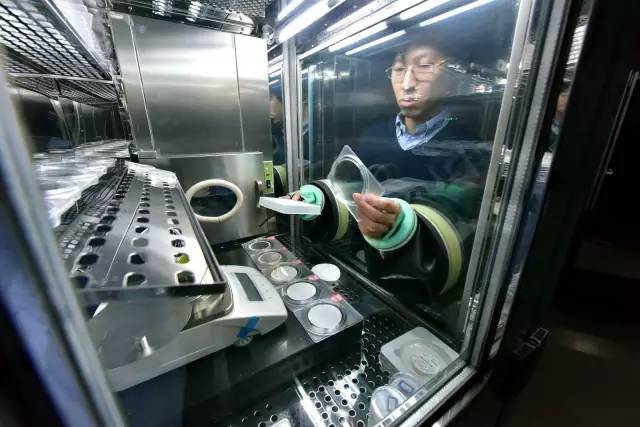

Technicians weigh filter paper using a constant temperature and humidity weighing box. Photography/Zhang Ke
The filter paper in my hand is already weighed heavy in the constant temperature and humidity weighing box next to it. When the exhaust gas passes through the filter paper, fine particles will be adsorbed on it, and the content of fine particles in the exhaust gas can be calculated by weighing, "said Ge Yunshan.
In the laboratory, technicians showed reporters four commonly used portable air quality detectors on the market. The principle of these detection instruments is the same, mostly using optical principles, and the content of fine particulate matter in exhaust gas is calculated. "Ge Yunshan said that the PM2.5 measured by these detection instruments is not the usual solid particles, but the total amount of liquid and solid particulate matter, with poor measurement accuracy and greatly affected by temperature.
In the video circulating online, the tester directly inserted the air inlet of the detector into the car exhaust pipe on the road, and after the car started, the exhaust directly rushed into the detector. The test results show that the levels of PM2.5 and PM10 in exhaust are lower than those in the air.
This does not mean that these instruments are problematic. It can also be said that these instruments are rigorous, but the methods of using them are not rigorous and exceed the scope of use, "said Dr. Wang Xin, a technician at the laboratory.
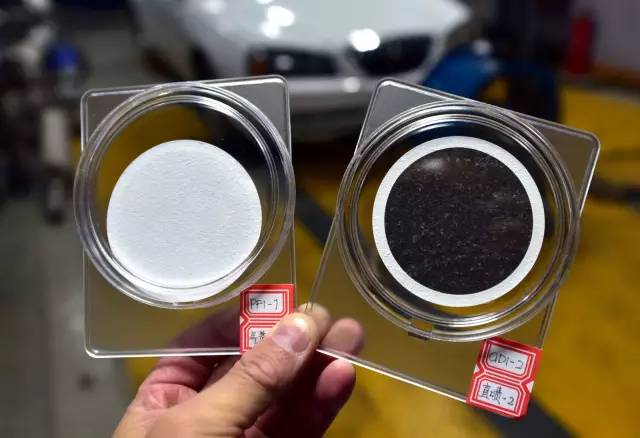


Ge Yunshan found the instruction manual for the same air quality monitoring device in the video for the reporter. The reporter saw that the precautions in the manual clearly mentioned, "When using this product for measurement, please place it in the area with slow air convection to prevent strong air flow from directly blowing from interfering with the detection results." "When the machine works normally, please avoid contact with alcohol substances such as alcohol, perfume, and high concentration hydrogen sulfide, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen, smoke and other gases, or it will lead to measurement errors or damage the host."



On the morning of the 5th, technicians conducted three experiments for reporters. Firstly, the laboratory air quality was tested using the same air quality detector as shown in the video. The results showed that PM2.5 and PM10 were 239 micrograms per cubic meter and 311 micrograms per cubic meter, respectively.
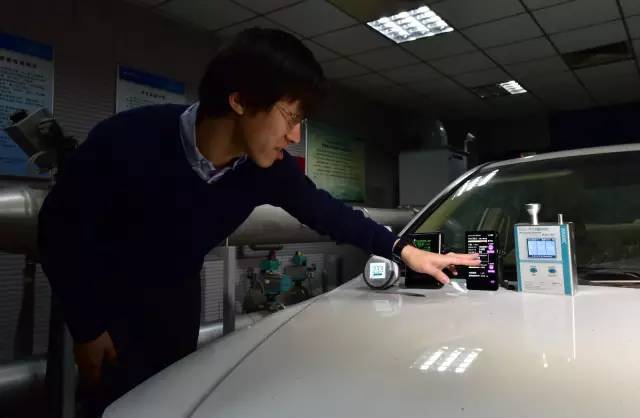
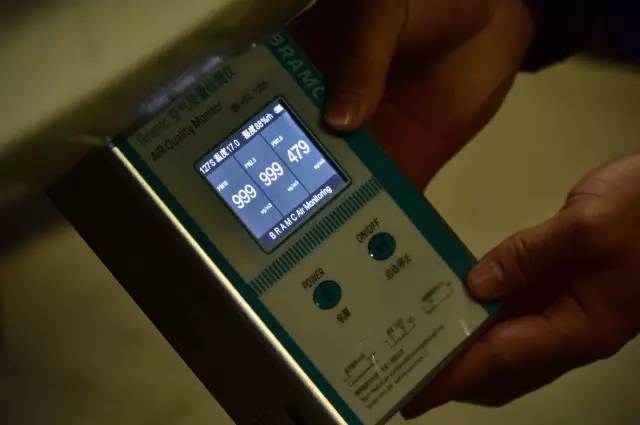



The first experiment was to start the car when it was cold, and then place the detector near the exhaust outlet for testing. The detector immediately "exploded". PM2.5 and PM10 are both 999 micrograms per cubic meter, and the humidity displayed by the detector also reaches 88%. At this time, a professional detector in the laboratory showed that the number of fine particles per cubic meter in the exhaust gas exceeded 140000, "while currently the number of fine particles per cubic meter in the air is only about 7000," Wang Xin said.
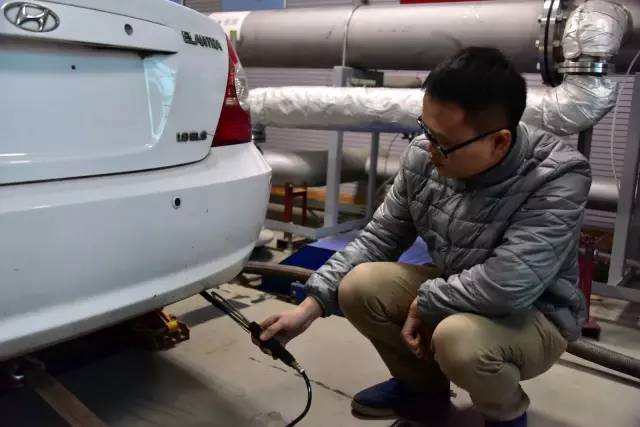
The second experiment was conducted by idling the vehicle while it was hot, and the detector was placed near the exhaust outlet and immediately "exploded", showing a humidity of up to 97%. The air inlet of the detector is made of aluminum surface, which is very prone to condensation. "When the detector was inserted into the exhaust pipe again, the value did not change much." It is very likely that water has entered the sampling pipe, blocking the gas. "Wang Xin shook the detector vigorously in the air, and indeed left a row of water droplets on the ground. The results of the laboratory professional detector show that there are 400000 fine particles per cubic meter in the exhaust gas.
For the third time, let's imitate the situation of 2500 RPM in the video. In fact, this cannot truly reflect the working conditions of the vehicle on the road, "said Wang Xin. The detector also "exploded" near the exhaust outlet and automatically shut down due to high humidity. After turning on again and placing it at the exhaust outlet, all data gradually returned to zero.
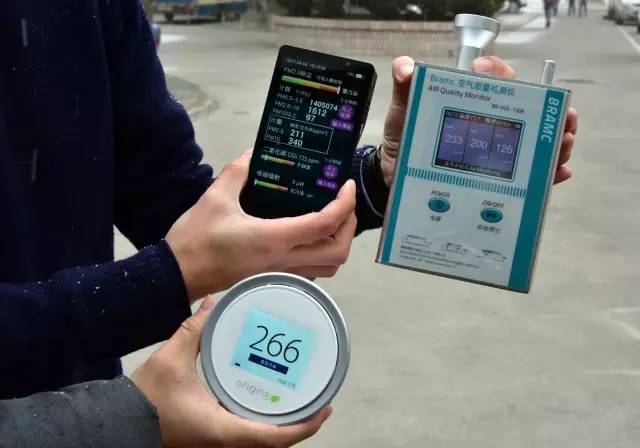


The video testing of gasoline vehicle exhaust pollution has unscientific testing methods and results, but the test results are highly misleading, "Ge Yunshan told reporters. The particle size of PM is very small, and strict requirements are placed on the testing instruments. The vast majority of portable PM instruments on the market cannot meet the requirements.
When the temperature is low, the water attached to the particles exists in the form of small droplets; when the temperature rises, the small droplets vaporize and the measurement results significantly decrease. "Ge Yunshan said that particle emissions should be diluted and cooled before measurement. Directly measuring high-temperature emissions with instruments for measuring atmospheric particulate matter can result in significant errors. The measurement results in room temperature air are not comparable to those directly measured on the exhaust pipe.
Wang Xin told reporters that PM2.5 in car exhaust is usually between 1000 and 2000 micrograms per cubic meter, and some are even higher. Even in the case of smog and air explosion, the exhaust is much dirtier than the air.
Ge Yunshan introduced that there are four ways for gasoline vehicles to emit pollution: exhaust pipe, refueling, evaporation, and crankcase. The main pollutants emitted include carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOX), hydrocarbons (HC), and fine particulate matter (PM).
Research shows that HC is mainly emitted through evaporation and refueling processes, with only about 10% of the total emissions from the exhaust pipes of National V vehicles, while the proportion of National III vehicles is around 50%. This is precisely what the emission standards in Europe and China have overlooked, so the newly issued National VI emission standard imposes strict control requirements on evaporative emissions and refueling process emissions
Researchers have found that gasoline cars emit high levels of pollutants during cold start, especially during low temperature cold start in winter. In addition, tire wear and road dust emissions during vehicle operation are both sources of PM2.5 in the atmosphere. The video circulating online only tested the concentration of particulate matter in the exhaust pipe of gasoline vehicles under high and low idle conditions, which cannot fully reflect the pollution emissions of gasoline vehicles.
Ge Yunshan told reporters that a comprehensive evaluation of the particulate matter emission level of automobiles needs to be measured from two indicators: one is the mass concentration of particulate matter, and the other is the number of particulate matter (PN). The video tests the mass concentration of particulate matter. The dynamic diameter of particulate matter emitted by gasoline vehicles is mainly below 100 nanometers (nm), and the mass of these small particles cannot be measured (only particles with a dynamic diameter of over 300 nm can be measured), and the mass concentration index cannot be characterized. Therefore, the mass concentration of primary particulate matter emitted by gasoline vehicles is very low, and the exhaust mass concentration tested in the video is consistent with the emission characteristics of gasoline vehicles.
In heavily polluted weather, the amount of fine particulate matter in the air is below 105 particles per cubic centimeter, while the amount of particulate matter emitted by gasoline vehicles is above 106 particles per cubic centimeter. After fine particulate matter in the air is drawn into the engine, some organic components will be burned off, and non combustible components will be broken into smaller particles. The moisture adsorbed by the particles will be separated through high-temperature gasification.
The smaller particles emitted by gasoline cars pose a greater direct threat to health, "said Ge Yunshan." Moreover, these small particles undergo a series of physical and chemical reactions in the air to adsorb moisture and other pollutants, and grow into PM2.5 particles in the atmosphere, exacerbating haze pollution.
It is worth mentioning that the pollutants emitted from the exhaust pipes of gasoline vehicles are mainly gaseous hydrocarbons (HC) and nitrogen oxides (NOX), which cannot be measured by portable PM instruments at the exhaust outlet. Research has shown that HC and NOX undergo a series of complex physical and chemical reactions in the atmospheric environment, especially under heavy haze weather conditions, rapidly converting into secondary particulate matter.
Among them, nitrogen oxides will be converted into secondary nitrate particles, while catalyzing the formation of secondary sulfate particles from sulfur dioxide. Hydrocarbons will be converted into secondary organic carbon particles. The conversion rate and conversion rate vary depending on the atmospheric environmental conditions, with conversion rates generally ranging from 25-50%.
These secondary particulate matter are the main components of smog in Beijing and other areas, posing a significant threat to human health. In recent years, air pollution in Beijing and many other regions has shown a predominance of secondary particulate matter, manifested by the gradual increase in concentrations of ozone (O3) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) Ge Yunshan said.
On the morning of the 5th, Hu Jingnan, a researcher at the Institute of Atmospheric Environment of the Chinese Academy of Environmental Sciences, told the First Financial Journalist that researchers from the Academy had used the filter membrane weighing method in the laboratory to sample and analyze the exhaust particulate matter emissions of seven light-duty gasoline vehicles in the National IV to National V stages.
The results showed that under the globally standardized light vehicle driving conditions (WLTC conditions), the particulate emission factors of these vehicles ranged from 0.3 to 4.5 milligrams per kilometer. There are significant differences in particulate emissions for vehicles with different technologies: the exhaust particulate emission factor of multi-point electronic fuel injection vehicles is between 0.3-2 milligrams per kilometer, which is equivalent to a mass concentration of particulate matter in the exhaust between 0.4-2.5 milligrams per cubic meter; The exhaust particulate matter emissions of direct injection vehicles are several times higher than those of intake injection vehicles, with an emission factor between 2-4.5 milligrams per kilometer, which is equivalent to a mass concentration of particulate matter in the exhaust between 2.5-6 milligrams per cubic meter.
Hu Jingnan said that compared to particulate matter, there is no significant difference in the emissions of gaseous pollutants (NOx, THC, and CO) from light-duty gasoline vehicles with different technologies. The nitrogen oxide NOx emission factor of light-duty gasoline vehicles is between 0.02-0.045 grams per kilometer, which is equivalent to a mass concentration of NOx in exhaust between 25-55 milligrams per cubic meter; The total hydrocarbon (THC) emission factor is between 0.02-0.07 grams per kilometer, which is equivalent to a mass concentration of THC in exhaust gas between 25-86 milligrams per cubic meter; The carbon monoxide (CO) emission factor is between 0.3-1.1 grams per kilometer, which is equivalent to a mass concentration of CO in the exhaust gas between 369-1353 milligrams per cubic meter.
The driving conditions of vehicles have a significant impact on the particulate matter emissions of gasoline vehicles. "Hu Jingnan introduced that through online measurement in the laboratory dilution channel (dilution ratio between 10-20 times), when the vehicle accelerates, the mass concentration of black carbon (BC is an important component of automobile exhaust particulate matter, and the black carbon content in the particulate matter emitted by direct injection vehicles is about 30-40%, and the black carbon content of multi-point electronic injection vehicles is generally below 10%) emissions often increases significantly compared to idle, especially for direct injection vehicles. The concentration of black carbon emitted from the exhaust of National IV direct injection gasoline vehicles at idle speed is significantly lower than that under acceleration and high-speed driving conditions.
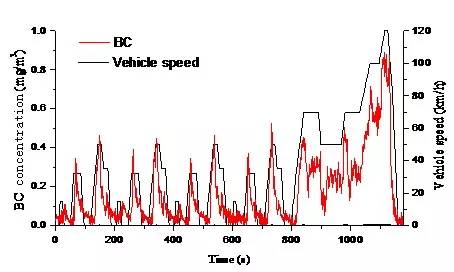
Hu Jingnan believes that motor vehicle exhaust emissions cannot be solely based on the direct emissions of particulate matter (primary particulate matter). NOx and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emissions also contribute to particulate matter, and these gaseous pollutants will react in the atmospheric environment to form PM2.5, commonly known as secondary particulate matter, which is an important source of PM2.5 during heavy pollution periods. Taking Beijing as an example, Hu Jingnan introduced that according to the analysis of atmospheric PM2.5 sources, the secondary particulate matter generated by the conversion of NOx and VOCs emitted by gasoline vehicles can account for about 5% -10% of PM2.5.
The harm of motor vehicle exhaust pollution is enormous. Motor vehicles have become the primary source of pollution in many large cities and are an important cause of haze pollution. "Ge Yunshan said that if car exhaust is really cleaner than haze air, then the air quality near transportation arteries would be better, but the actual situation is not like that.
Research shows that the closer the distance to the transportation line, the more severe the air pollution, and the farther the distance, the better the air quality. If car exhaust can really be cleaner than air, how could tragedies often occur in China where people are poisoned to death by exhaust in closed cars
Ge Yunshan told reporters that from the perspective of motor vehicle environmental management, the prevention and control of motor vehicle pollution should indeed prioritize the control of vehicles with high emissions and heavy pollution, including diesel trucks, buses, municipal, environmental sanitation and logistics vehicles, as well as old gasoline vehicles with long driving distances such as taxis.
In addition, the video also raises a thought-provoking question: can we create cars with cleaner emissions to purify the air on hazy days? "Ge Yunshan said. This is a dream of the automotive industry and also the expectation of many environmentalists and car owners. Some advanced international companies are indeed working hard to develop cars with cleaner emissions. Although some companies claim to have been able to manufacture cars with emissions cleaner than air, the overall level of the world's automotive industry is still far from reaching such a level
